依赖管理
- 在所有的Spring Boot项目中,我们可以看到,在pom.xml 文件中都会有一个parent 标签,如下所示。
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.9</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
当我们点进spring-boot-starter-parent 这个项目时,可以看到它的父项目为
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.4.9</version>
</parent>
再次点击spring-boot-dependencies 项目,可以看到
在这个项目中几乎声明了所有开发中常用的依赖的版本号,这就是Spring Boot的默认的依赖管理,自动版本仲裁机制。
- 无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁
1、引入依赖默认都可以不写版本
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3.1</version>
</dependency>
- 可以修改默认版本号
1、查看spring-boot-dependencies里面规定当前依赖的版本 用的 key。然后在当前项目里面重写配置
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>
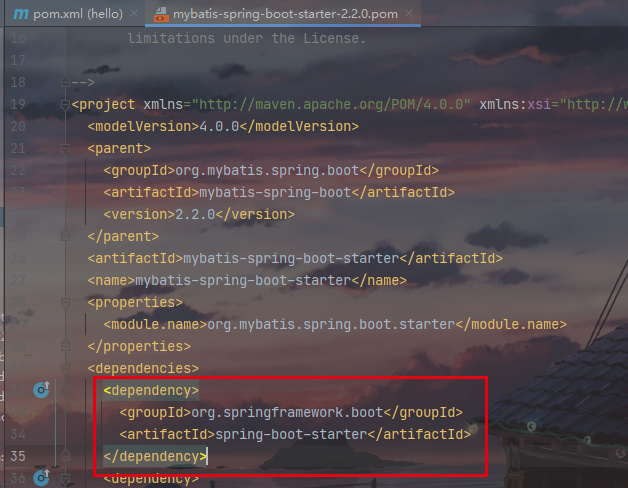
2. 直接申明版本号
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
- 开发导入starter场景启动器
1、见到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就是指的某种场景
2、只要引入starter,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖我们都自动引入
3、SpringBoot所有支持的场景
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
4、见到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方为我们提供的简化开发的场景启动器。例如上面提到的mybatis-spring-boot-starter
5、所有场景启动器最底层的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.4.9</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
例如:
自动配置
在昨天的示例程序中,我们可以发现,我们并没有启动Tomcat ,没有配置web.xml文件,就能够直接访问,这就是Spring Boot的自动装配。
- Tomcat的自动引入
- 因为引入了spring-boot-starter-web 依赖,同时也是上面所说的启动器,在这个启动器中有spring-boot-starter-tomcat。
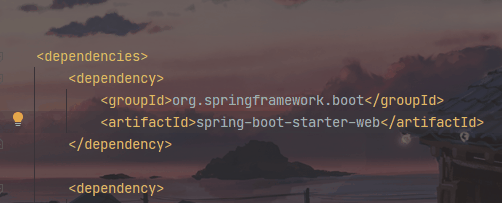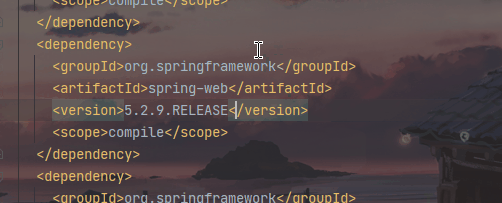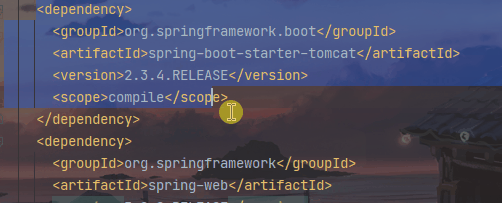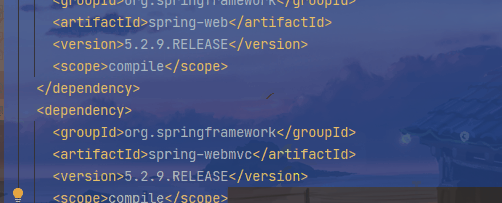
- 自动配好SpringMVC
- 通过代码查看Spring Boot中初始化的组件
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、返回我们IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
//2、查看容器里面的组件
String[] names = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
启动项目,可以看到有很多之前Spring MVC需要主动配置的组件已经默认加载进去了
如拦截所有请求的dispatcherServlet、字符编码处理的characterEncodingFilter 过滤器。
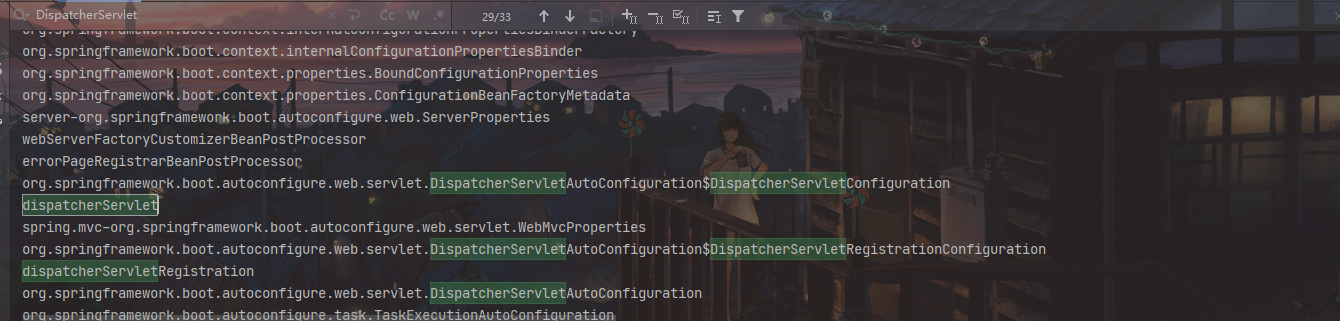
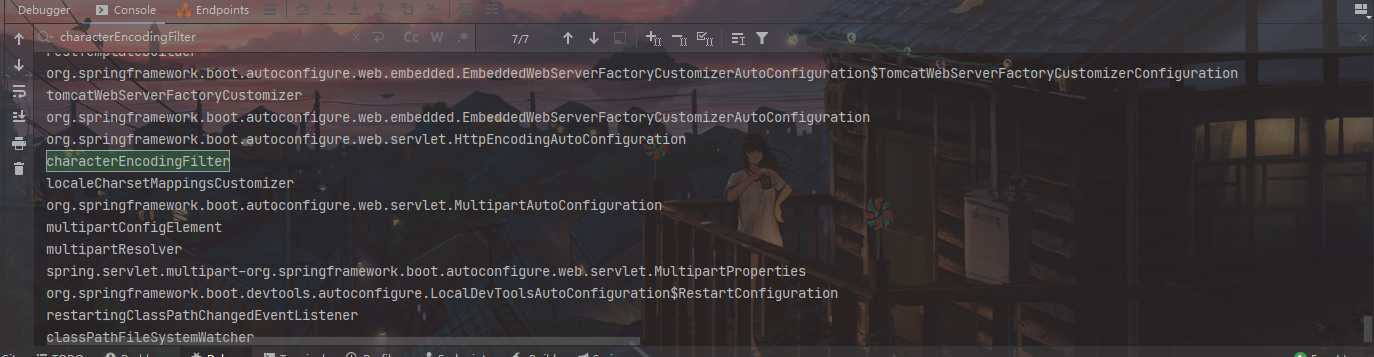
spring-boot-starter-web 启动器帮我们配置好了几乎所有web 开发中常见场景。
- 默认的包结构
- 在之前,我们想要将controller包下的类加载进来,还需要配置包扫描路径,而Spring Boot 中主程序所在包及其下面的所有子包里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来
- 如果想要改变扫描路径,可以通过修改主程序类上的注解
- @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.atguigu")
- @SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
@SpringBootApplication
等同于
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.boot")
的集合
- 各种配置拥有默认值
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:上传文件的最大值maxFileSize默认值为会MultipartProperties的
private DataSize maxFileSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(1L); - 配置文件的值最终会绑定每个类上,如:
server.port=8888这行配置会映射到ServerProperties这个类上。这个类会在容器中创建对象
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:上传文件的最大值maxFileSize默认值为会MultipartProperties的
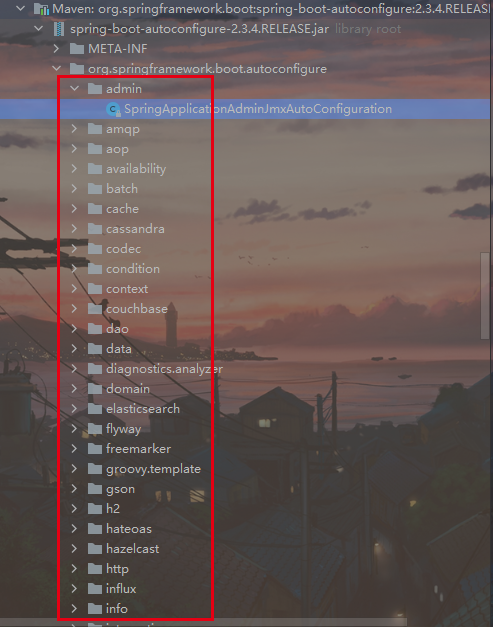
- 按需加载所有自动配置项
- 在Spring Boot 中有许多的starter 启动器
- 但是Spring 做了按需加载,只有引入了某个场景这个场景的自动配置才会开启
- SpringBoot所有的自动配置功能都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面
总结
以上就是Spring Boot 的特点,也可以说是优点,正是有了Spring Boot的自动装配,才能让我们的开发变得如此简单,博客主要用作复习学习,如果有小伙伴看到后看不懂,可以在下面留言,我会尽量进行解答。
后面会进行Spring Boot 自动配置的原理的复习。
声明
这篇博客基于B站尚硅谷的视频:雷丰阳2021版SpringBoot2零基础入门springboot全套完整版(spring boot2)编写。
在此先表示感谢。
如有侵权,请联系我删除。

